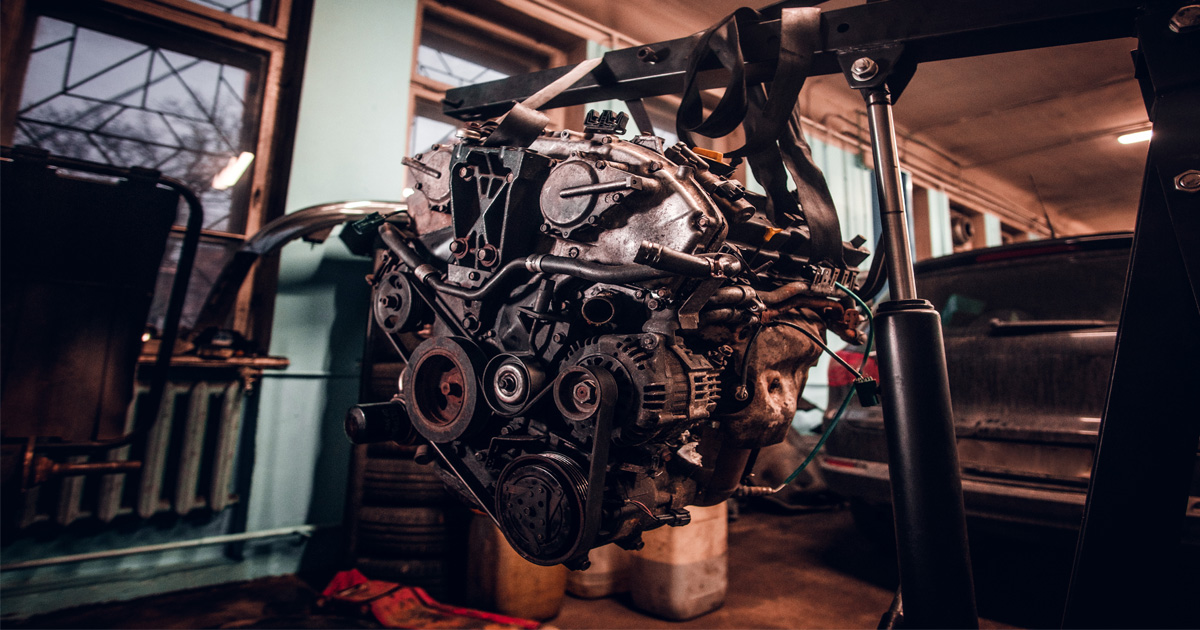
An automobile engine is a complex machine that converts fuel into mechanical energy to power a vehicle. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
1. The Engine’s Core Principle: The Internal Combustion Process
Most car engines are internal combustion engines (ICEs), which means they burn fuel inside a confined space (cylinder) to produce power. The most common type is the four-stroke engine, which operates in four distinct steps:
2. The Four-Stroke Cycle
Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens, and the piston moves down, allowing a mixture of air and fuel to enter the cylinder.
Compression Stroke: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture, making it more explosive.
Power Stroke: A spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing a small explosion. This forces the piston downward, generating power.
Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up, pushing out burned gases.
3. Key Engine Components
Cylinders: Where combustion happens (usually 4, 6, or 8 in most cars).
Pistons: Move up and down inside the cylinders to transfer power.
Crankshaft: Converts the piston’s up-and-down motion into rotational motion to turn the wheels.
Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves.
Spark Plug: Creates a spark to ignite the fuel.
Fuel Injector/Carburetor: Delivers the right amount of fuel into the cylinder.
Cooling System: Prevents overheating (radiator, coolant, water pump).
Lubrication System: Reduces friction (engine oil).